1 day / second
0.5 AU
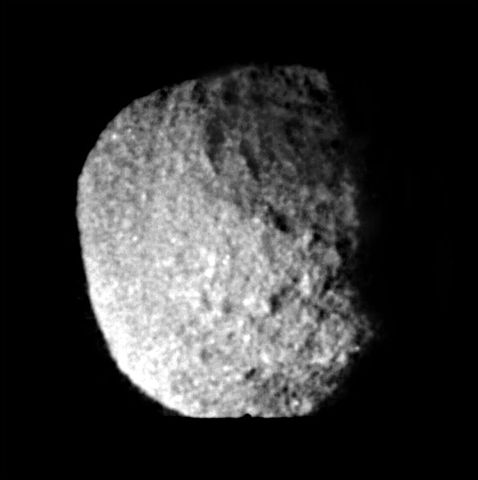
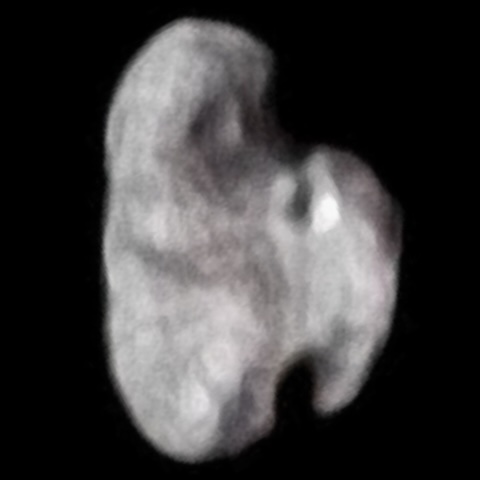
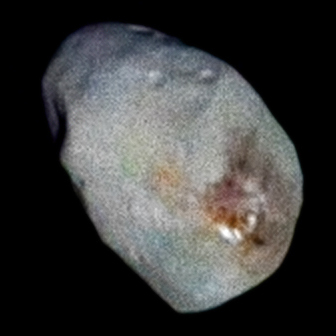
Hydra
Moon of Pluto
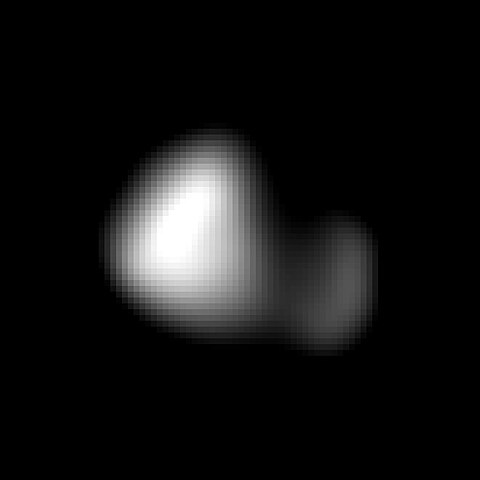
A tiny, irregularly shaped moon in a chaotic orbit around Pluto, discovered in 2005 as part of the same survey that found Nix and subsequently named after the nine-headed serpent from Greek mythology.
Key Facts
learn more | Wikipedia |
mass | 3.0100e+16 kg |
radius | 19 km |
semi-major axis | 64,738 km |
eccentricity | 0.006 |
inclination | 0.242º |
longitude of the ascending node | 189.7º |
argument of periapsis | 192.2º |
orbital period | 40.627 days |
surface gravity | 0.001 g |
discovery date | May 15, 2005 |
discovered by | Marc Buie and Alan Stern using Hubble Space Telescope |
name origins | Named after Hydra, the mythological many-headed serpent |
albedo | 0.35 |
dimensions | Approximately 115 km long (based on radius of 57.5 km) |
material composition | Suspected to be primarily water ice |
Parent Dwarf Planet
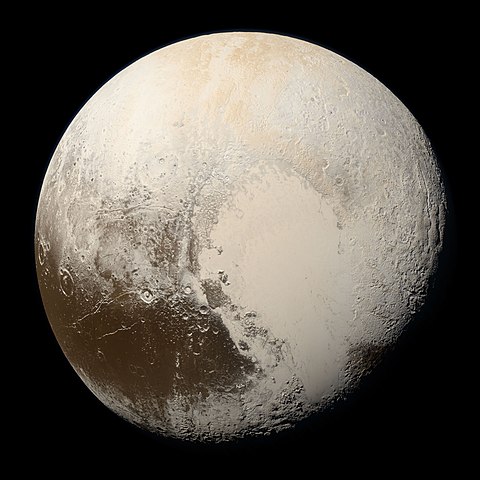
134340 Pluto
A frigid dwarf planet orbiting in the distant Kuiper Belt, characterized by its reddish-brown coloring, prominent heart-shaped plain, thin nitrogen atmosphere, and five moons including its largest companion Charon.
Spacecraft Visits
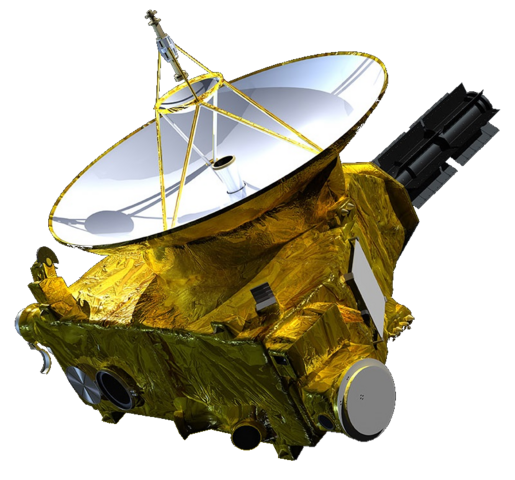
New Horizons
Flyby
Launched in 2006, visited in 2015
New Horizons captured detailed images of Hydra during its historic Pluto system flyby on July 14, 2015, revealing the moon to be an irregular, elongated object approximately 55 kilometers in length.