1 day / second
0.5 AU
Luna (The Moon)
Moon of Earth
Earth's only natural satellite is a large, tidally-locked moon that formed from debris ejected during a massive collision between Earth and a Mars-sized body early in the Solar System's history.
Key Facts
learn more | Wikipedia |
mass | 7.3420e+22 kg |
radius | 1,737.4 km |
semi-major axis | 384,400 km |
eccentricity | 0.055 |
inclination | 5.145º |
longitude of the ascending node | 125.08º |
argument of periapsis | 318.15º |
orbital period | 27.452 days |
sidereal rotation period | 27.322 days |
axial tilt | 6.687º |
surface gravity | 0.166 g |
discovery date | Visible since prehistoric times |
name origins | Named after Proto-Indo-European root "mē" meaning "to measure" (due to use measuring months) |
rotation | Tidally locked to Earth |
albedo | 0.136 |
material composition | Rocky with significant iron and magnesium. Surface covered in lunar soil (regolith) |
density | 3.344 g/cm³ |
Gallery
Parent Planet
Earth
A life-bearing terrestrial planet with a significant atmosphere, active geology, and a large moon, distinguished by its vast oceans of liquid water and diverse ecosystems that make it unique in the Solar System.
Spacecraft Visits
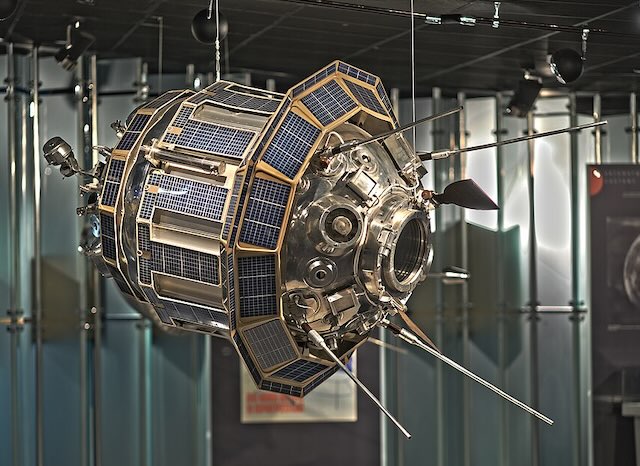
Luna 2
Impactor
Launched in 1959, impacted in 1959
Luna 2 became the first spacecraft to reach the Moon's surface on September 14, 1959, making a high-speed impact near the Palus Putredinis region.
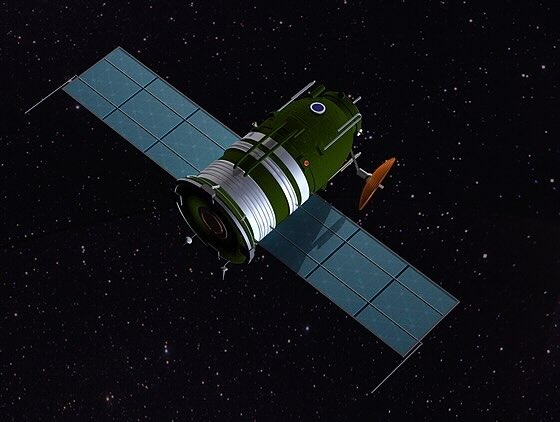
Luna 3
Flyby
Launched in 1959, visited in 1959
Luna 3 made history by capturing the first-ever photographs of the Moon's far side during its flyby on October 7, 1959, revealing previously unseen lunar features to human eyes.
Zond 5
Flyby
Launched in 1968, visited in 1968
Zond 5 became the first spacecraft to circle the Moon and return safely to Earth, carrying turtles, wine flies, mealworms, plants, seeds and bacteria on its historic 6-day circumlunar journey in September 1968.
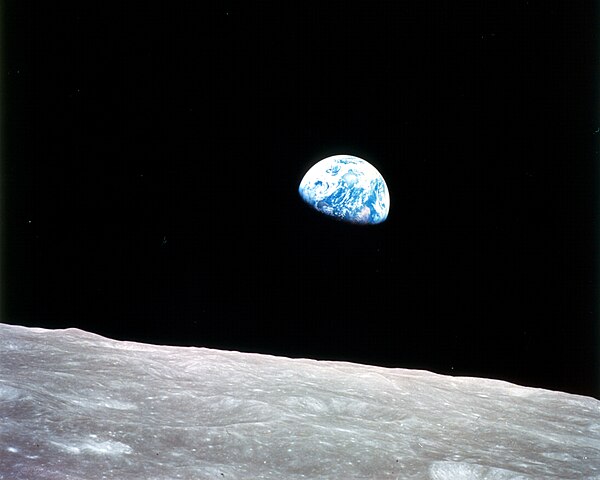
Apollo 8
Orbiter
Launched in 1968, entered orbit in 1968
Crewed by Frank Borman, James Lovell, William Anders
Apollo 8 became the first crewed spacecraft to leave Earth's orbit, reach the Moon, and orbit another celestial body during its historic 20-hour lunar orbit beginning on December 24, 1968.
Apollo 10
Orbiter
Launched in 1969, entered orbit in 1969
Crewed by Thomas Stafford, Gene Cernan, John Young
Apollo 10 performed a complete dress rehearsal for the first Moon landing, descending to within 8.4 nautical miles of the lunar surface in the Lunar Module "Snoopy" while testing all systems and procedures except the actual landing.
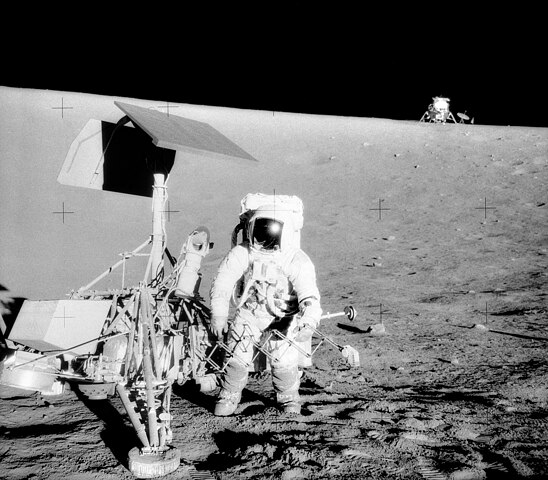
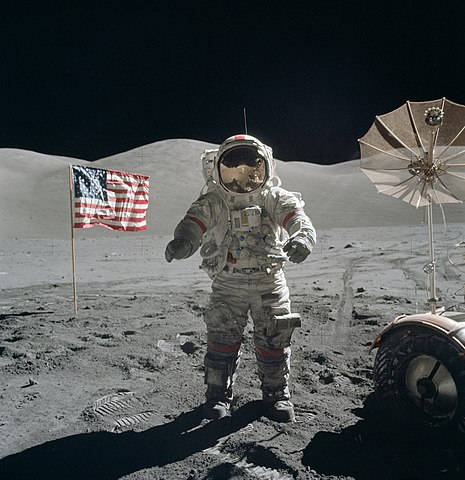
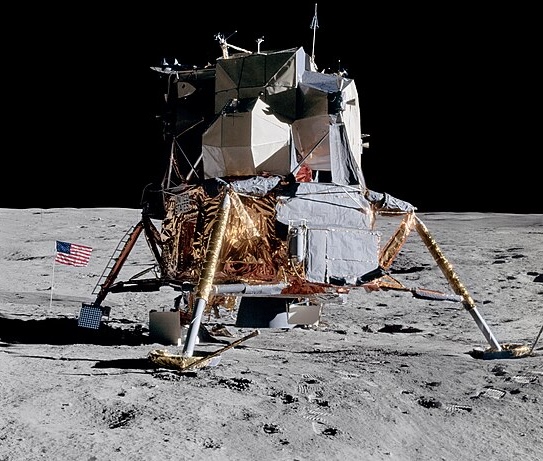
Apollo 11
Lander
Launched in 1969, landed in 1969
Crewed by Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin, Michael Collins
Apollo 11 became the first manned spacecraft to land on the Moon on July 20, 1969, when Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin landed on Mare Tranquillitatis for their historic 21-hour stay.
Apollo 12
Lander
Launched in 1969, landed in 1969
Crewed by Pete Conrad, Alan Bean, Richard Gordon
Apollo 12 achieved the second crewed Moon landing on November 19, 1969, with astronauts Pete Conrad and Alan Bean touching down in Oceanus Procellarum just 600 feet from the Surveyor 3 probe's landing site.
Apollo 13
Flyby
Launched in 1970, visited in 1970
Crewed by Jim Lovell, Jack Swigert, Fred Haise
After suffering a catastrophic oxygen tank explosion en route to the Moon, Apollo 13 used lunar gravity for a "slingshot" maneuver to return safely to Earth in what became known as a "successful failure."
Lunokhod 1
Rover
Launched in 1970, landed in 1970
Lunokhod 1 became the first successful robotic rover on another world, operating for 322 Earth days on the lunar surface and covering 10.5 kilometers while transmitting more than 20,000 images and conducting soil analyses.
Apollo 14
Lander
Launched in 1971, landed in 1971
Crewed by Alan Shepard, Stuart Roosa, Edgar Mitchell
Apollo 14 landed in the Fra Mauro highlands on February 5, 1971, where astronauts Alan Shepard and Edgar Mitchell conducted two moonwalks, collected 94 pounds of lunar samples, and famously hit two golf balls across the lunar surface.
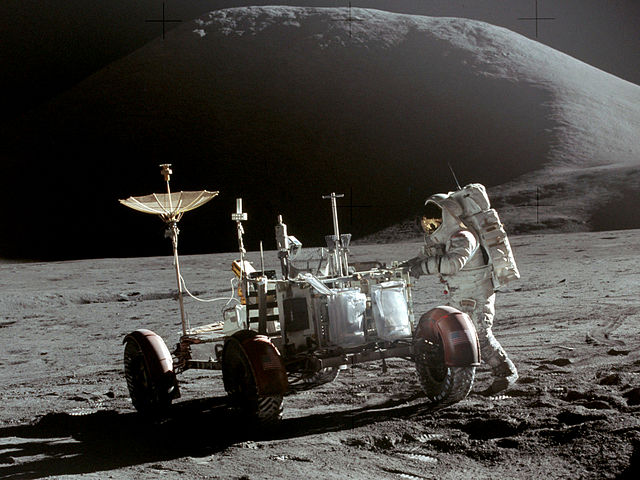
Apollo 15
Lander
Launched in 1971, landed in 1971
Crewed by David Scott, Alfred Worden, James Irwin
Apollo 15 landed in the Hadley-Apennine region of the Moon on July 30, 1971, where astronauts David Scott and James Irwin conducted three EVAs and became the first to use the Lunar Roving Vehicle during their 67-hour surface stay.
Apollo 16
Lander
Launched in 1972, landed in 1972
Crewed by John Young, Ken Mattingly, Charlie Duke
Apollo 16 landed in the Descartes Highlands on April 21, 1972, where astronauts John Young and Charles Duke spent 71 hours on the lunar surface, conducting geological surveys and collecting 95.8 kg of rock samples.
Apollo 17
Lander
Launched in 1972, landed in 1972
Crewed by Gene Cernan, Ronald Evans, Jack Schmitt
Apollo 17 conducted the final lunar landing of the Apollo program, with astronauts Eugene Cernan and Harrison Schmitt spending three days exploring the Taurus-Littrow valley while conducting extensive geological studies and collecting 110.5 kg of samples.
Hiten
Orbiter
Launched in 1990, entered orbit in 1993
Hiten became Japan's first lunar probe by entering lunar orbit on October 2, 1991, and remained in orbit until it impacted the Moon's surface during a controlled descent on April 10, 1993.
Nozomi
Gravity Assist
Launched in 1998, visited in 1998
Nozomi performed two gravity assist maneuvers past the Moon in September and December 1998 to increase its velocity for its journey to Mars, though the spacecraft ultimately failed to enter Mars orbit due to electrical problems.
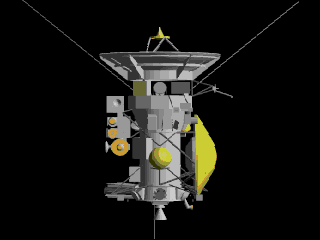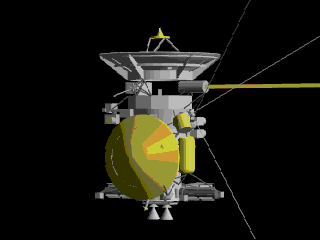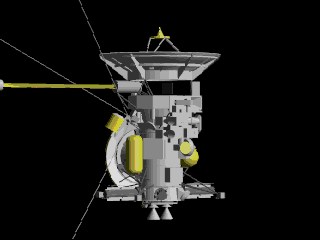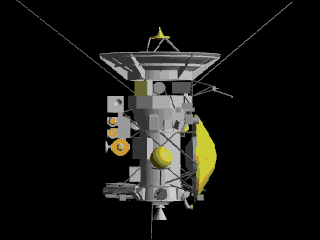
Cassini
Flyby
Launched in 1997, visited in 1999
Cassini performed a gravity assist flyby of the Moon at a distance of 6,200 kilometers on August 18, 1999, as part of its complex trajectory to reach Saturn.
SMART-1
Orbiter
Launched in 2003, entered orbit in 2004
SMART-1 orbited the Moon from November 2004 to September 2006, using an innovative ion engine for propulsion and conducting comprehensive mapping of lunar composition and surface features before deliberately impacting the lunar surface.
SELENE
Orbiter
Launched in 2007, entered orbit in 2007
SELENE (Kaguya) orbited the Moon from October 2007 to June 2009, conducting detailed surveys of lunar composition and topography with its 14 science instruments before making a controlled impact near Gill crater.
Chang'e 1
Orbiter
Launched in 2007, entered orbit in 2007
Chang'e 1 orbited the Moon for 16 months, completing the first lunar probe mission by China and producing a high-resolution 3D map of the lunar surface before being intentionally impacted into the Moon on March 1, 2009.
Chang'e 2
Orbiter
Launched in 2010, entered orbit in 2010
Chang'e 2 orbited the Moon for 8 months in 2010-2011, capturing high-resolution imagery and mapping the surface before departing for an extended mission to asteroid 4179 Toutatis.
Chang'e 4
Lander
Launched in 2018, landed in 2019
Chang'e 4 became the first spacecraft to achieve a soft landing on the far side of the Moon on January 3, 2019, touching down in the Von Kármán crater and deploying the Yutu-2 rover to explore the lunar surface.
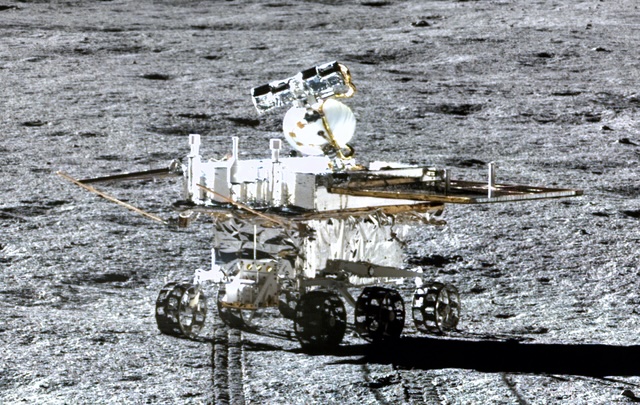
Yutu-2
Rover
Launched in 2018, landed in 2019
The Yutu-2 rover became the first spacecraft to land on the far side of the Moon on January 3, 2019, touching down in the Von Kármán crater as part of the Chang'e 4 mission.
Chang'e 5
Lander
Launched in 2020, landed in 2020
Chang'e 5 successfully landed in the Mons Rümker region of Oceanus Procellarum on December 1, 2020, collecting 1.731 kg of lunar samples which were returned to Earth on December 16, marking the first lunar sample return since 1976.
Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM)
Lander
Launched in 2023, landed in 2024
SLIM achieved a successful but tipped-over landing on the lunar surface near Shioli crater on January 19, 2024, demonstrating precision landing technology despite experiencing power issues due to its solar panels facing the wrong direction.
Chang'e 6
Lander
Launched in 2024, landed in 2024
The robotic Chang'e 6 lander will attempt the first-ever landing on the Moon's far side in 2024, aiming to collect and return lunar samples from the South Pole-Aitken basin.
Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer
Flyby
Launched in 2023, visited in 2024
The Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) performed a lunar-Earth gravity assist flyby on April 23, 2024, as part of its eight-year journey to reach the Jovian system.