1 day / second
0.5 AU
Mars
Planet
A cold, dusty red planet with massive extinct volcanoes, deep canyons, frozen polar caps, and evidence of ancient water flows, making it the most Earth-like planet in the Solar System.
Key Facts
orbital regime | Inner System |
learn more | Wikipedia |
mass | 6.4171e+23 kg |
radius | 3,389.5 km |
hill radius | 982,693 km |
semi-major axis | 1.524 AU |
eccentricity | 0.094 |
inclination | 1.85º |
longitude of the ascending node | 49.579º |
argument of periapsis | 286.502º |
orbital period | 1.881 years |
sidereal rotation period | 1.026 days |
axial tilt | 25.19º |
surface gravity | 0.38 g |
discovery date | Visible to naked eye since ancient times |
name origins | Named after Mars, the Roman god of war (and Ares, the Greek equivalent) |
albedo | 0.17-0.25 |
material composition | Rock and iron oxide (giving its reddish color), with polar ice caps |
density | 3.933 g/cm³ |
Gallery
Major Moons
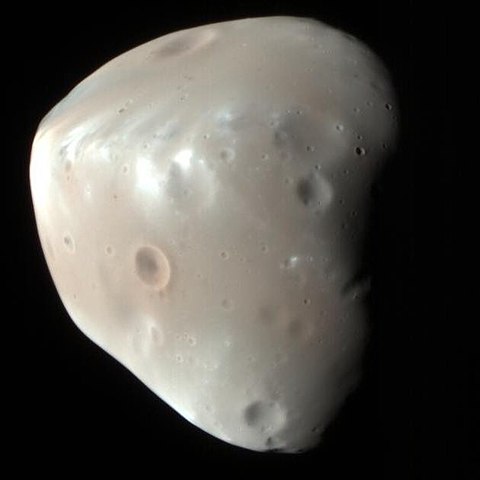
Phobos
A small, heavily cratered moon that orbits so close to Mars that it will eventually break apart or crash into the planet due to tidal forces.
Deimos
A tiny, irregularly shaped moon that orbits Mars every 30.3 hours at a distance of 23,460 km above the planet's surface.
Spacecraft Visits
Mariner 4
Flyby
Launched in 1964, visited in 1965
Mariner 4 completed the first successful flyby of Mars on July 14-15, 1965, capturing 22 close-range photographs that revealed a cratered, moonlike surface and helped dispel speculation about possible artificial canals on the planet.
Mars 3
Lander
Launched in 1971, landed in 1971
Mars 3 became the first spacecraft to achieve a soft landing on Mars on December 2, 1971, but transmitted data for only 20 seconds before failing due to a powerful dust storm.
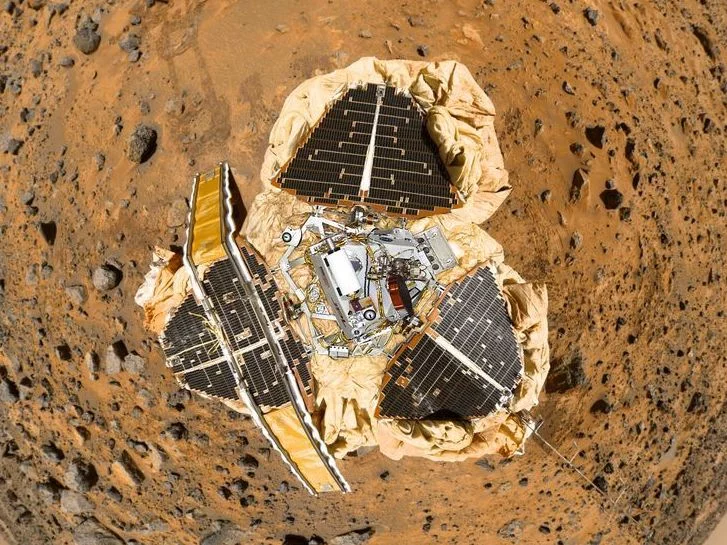

Mars Pathfinder
Lander
Launched in 1996, landed in 1997
The Mars Pathfinder landed in Ares Vallis on July 4, 1997, deploying the Sojourner rover which explored the Martian surface for 83 sols, analyzing rocks and returning over 16,500 images.
Sojourner
Rover
Launched in 1996, landed in 1997
The small rover became the first wheeled vehicle to explore Mars, traveling 100 meters during its 83-day mission while analyzing rocks and testing new technologies as part of the Mars Pathfinder mission.
Mars Global Surveyor
Orbiter
Launched in 1996, entered orbit in 1997
Mars Global Surveyor reached Mars orbit on September 11, 1997, beginning a highly successful mapping mission that lasted nearly a decade and revealed evidence of ancient water features across the planet's surface.
Nozomi
Flyby
Launched in 1998, visited in 2003
Nozomi failed to enter Mars orbit on December 14, 2003, due to electrical failures and propulsion problems that had plagued the mission since its 1998 launch, becoming Japan's first unsuccessful Mars mission.
Mars Express
Orbiter
Launched in 2003, entered orbit in 2003
Mars Express entered orbit around Mars on December 25, 2003, where it continues to operate today while studying the planet's atmosphere, surface features, and searching for subsurface water ice.
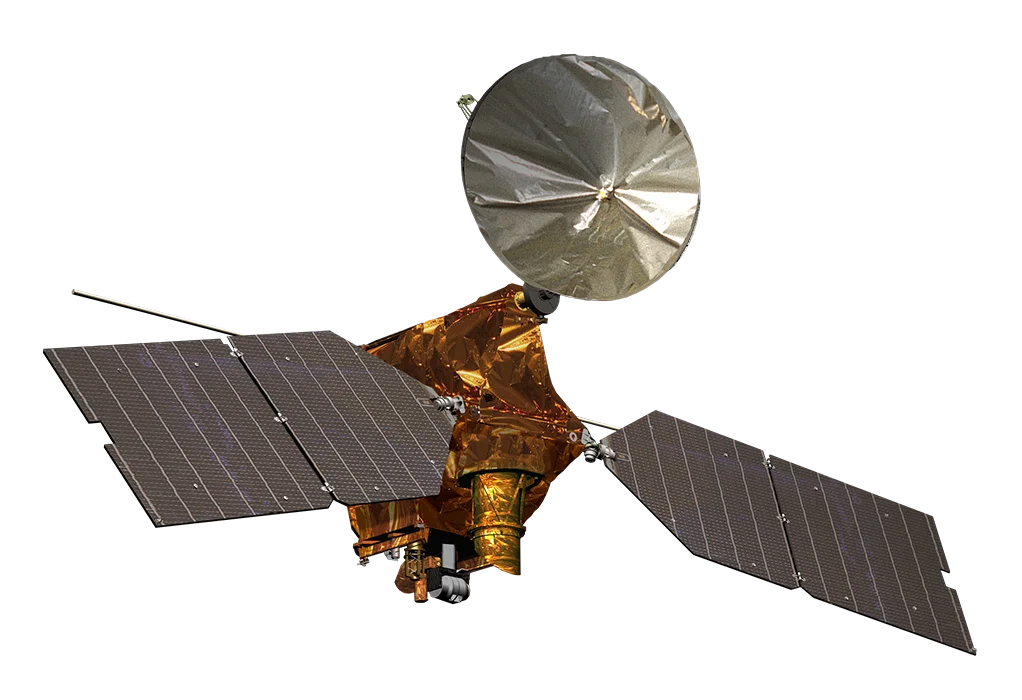

Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
Orbiter
Launched in 2005, entered orbit in 2006
The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter successfully entered Mars orbit on March 10, 2006, beginning a mission to study the planet's geology and climate that continues to this day, capturing high-resolution images of the surface and helping identify potential landing sites for future missions.
Rosetta
Gravity Assist
Launched in 2004, visited in 2007
Rosetta performed a gravity assist flyby of Mars on February 25, 2007, passing within 250 kilometers of the surface during a highly precise maneuver that helped adjust its trajectory towards comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko.
Dawn
Gravity Assist
Launched in 2007, visited in 2009
Dawn made a gravity assist flyby of Mars on February 17, 2009, using the planet's gravitational field to modify its trajectory and save fuel on its journey to Vesta and Ceres.
Curiosity
Rover
Launched in 2011, landed in 2012
The Curiosity rover landed in Gale Crater on Mars on August 6, 2012, beginning a mission to explore Mars' climate and geology that continues to operate after traveling over 17 miles across the Martian surface.
MAVEN
Orbiter
Launched in 2013, entered orbit in 2014
MAVEN entered Mars orbit on September 21, 2014, beginning its mission to study the Red Planet's upper atmosphere, ionosphere, and interactions with the Sun and solar wind.
InSight
Lander
Launched in 2018, landed in 2018
InSight landed in Elysium Planitia on November 26, 2018, where it studied Mars' interior structure and seismic activity for nearly four years until its solar panels became covered in dust, ending the mission in December 2022.
Tianwen-1
Orbiter
Launched in 2020, entered orbit in 2021
Tianwen-1 entered Mars orbit on February 10, 2021, becoming the first Mars mission to successfully complete an orbiter-rover combination on its first attempt, with the Zhurong rover exploring Utopia Planitia for 358 days.
Perseverance
Rover
Launched in 2020, landed in 2021
The six-wheeled Perseverance rover landed in Mars' Jezero Crater on February 18, 2021, beginning its mission to search for signs of ancient microbial life and collect rock samples for future return to Earth.
Ingenuity
Helicopter
Launched in 2020, started flying in 2021
Ingenuity made history as the first powered aircraft to make a controlled flight on another planet, completing 39 successful flights on Mars after its initial flight on April 19, 2021.
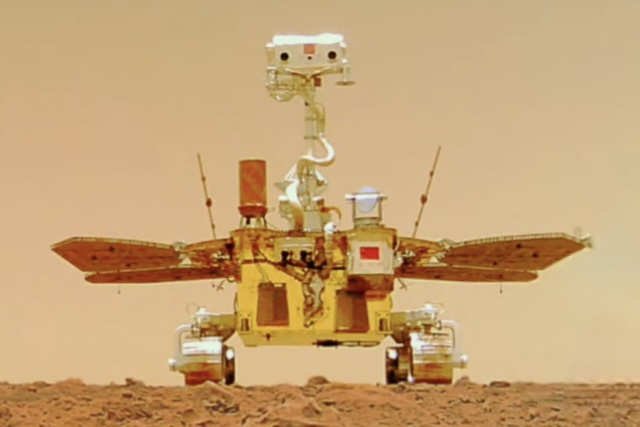
Zhurong
Rover
Launched in 2020, landed in 2021
The Zhurong rover successfully landed in Mars' Utopia Planitia region on May 14, 2021, becoming China's first Mars rover and operating for 347 days before entering dormancy during a global dust storm.
Europa Clipper
Gravity Assist
Launched in 2024, visited in 2025
Europa Clipper will perform a gravity assist maneuver at Mars on February 1, 2025, using the planet's gravitational field to adjust its trajectory toward Jupiter during its interplanetary journey.
Hera
Gravity Assist
Launched in 2024, visited in 2025
Hera performed a gravity assist maneuver at Mars in March 2025, using the planet's gravitational field to adjust its trajectory toward the binary asteroid system Didymos for its planned arrival in late 2026.