1 day / second
0.5 AU
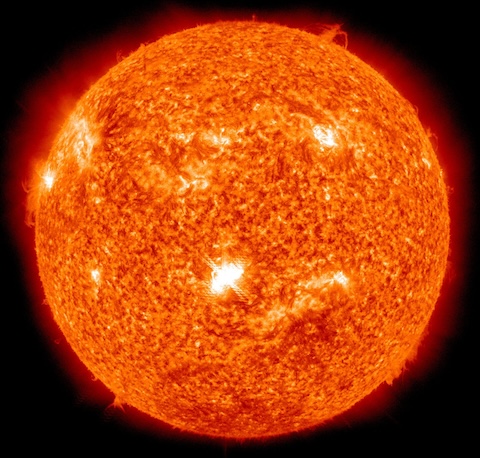
Sol (The Sun)
Star
A massive yellow dwarf star that contains 99.86% of the Solar System's mass and powers almost all life and weather on Earth through nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core.
Key Facts
learn more | Wikipedia |
mass | 1.9885e+30 kg |
radius | 695,700 km |
sidereal rotation period | 25.38 days |
axial tilt | 7.25º |
surface gravity | 27.961 g |
age | 4.6 billion years |
star type | G-type main-sequence star (yellow dwarf) |
temperature (center) | 15,700,000 K |
temperature (corona) | 5,000,000 K |
discovery date | Visible since prehistoric times |
material composition | Primarily hydrogen (73%) and helium (25%) with trace amounts of heavier elements |
density | 1.41 g/cm³ (average) |
Major Planets
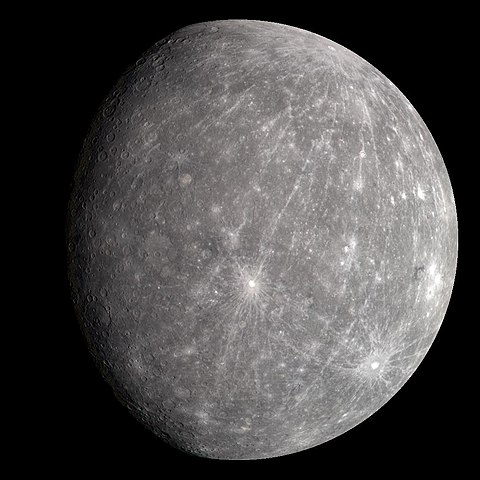
Mercury
The smallest and innermost planet in our Solar System, Mercury is a heavily cratered, airless world that experiences extreme temperature swings due to its proximity to the Sun and lack of atmosphere.
Venus
A scorching hot rocky planet with thick clouds of sulfuric acid, crushing atmospheric pressure 90 times that of Earth, and a surface hot enough to melt lead due to a runaway greenhouse effect.
Earth
A life-bearing terrestrial planet with a significant atmosphere, active geology, and a large moon, distinguished by its vast oceans of liquid water and diverse ecosystems that make it unique in the Solar System.
Mars
A cold, dusty red planet with massive extinct volcanoes, deep canyons, frozen polar caps, and evidence of ancient water flows, making it the most Earth-like planet in the Solar System.
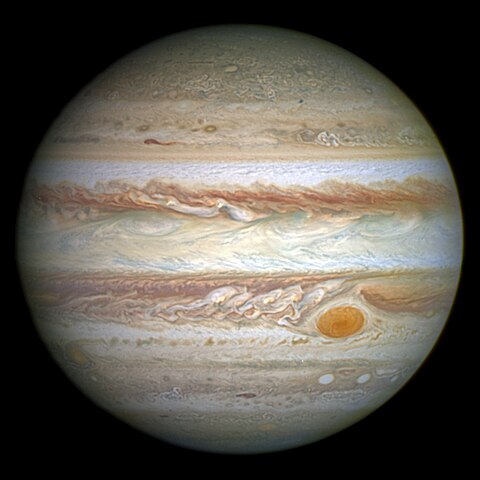
Jupiter
The largest planet in the Solar System, Jupiter is a gas giant with distinctive bands of swirling clouds, a powerful magnetic field, at least 95 moons, and an ongoing storm called the Great Red Spot that has raged for centuries.
Saturn
A massive ringed gas giant with a distinctive yellow-orange hue, known for its extensive system of icy rings and more than 80 moons, including Titan, the only moon in the Solar System with a thick atmosphere.
Uranus
A cold, blue-green ice giant planet tipped nearly sideways on its axis, with a set of narrow rings and a family of at least 27 moons named after literary characters.
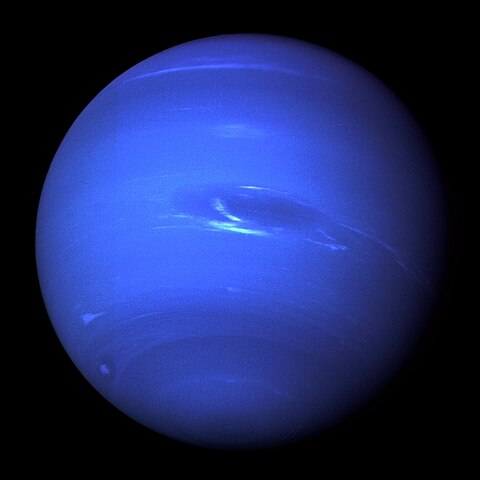
Neptune
The eighth and most distant planet, Neptune is a cold, windy ice giant with a vivid blue color, powerful storms, supersonic winds reaching 1,200 mph, and a collection of 14 known moons including the geologically active Triton.
Spacecraft Visits
Ulysses
Flyby
Launched in 1990, visited in 1994
Ulysses became the first spacecraft to study the Sun's polar regions during its solar flybys in 1994 and 1995, reaching latitudes of up to 80 degrees above and below the solar equator.
Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO)
Orbiter
Launched in 1995, entered orbit in 1996
SOHO established a halo orbit around the Sun-Earth Lagrange point L1 in 1996, where it continues to study solar physics and space weather through detailed observations of the Sun's outer corona, interior, and solar wind.
Parker Solar Probe
Orbiter
Launched in 2018, entered orbit in 2018
Parker Solar Probe launched on a historic mission to study the Sun's corona and solar wind, making its first close approach on November 5, 2018, flying within 15 million miles of the solar surface.
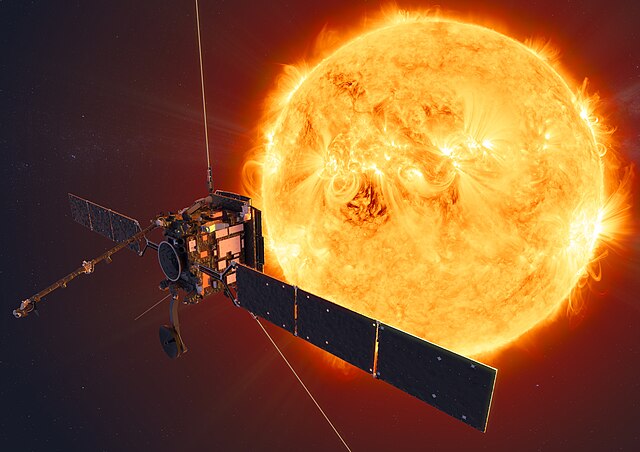
Solar Orbiter
Orbiter
Launched in 2020, entered orbit in 2020
Solar Orbiter began its mission to study the Sun's polar regions and inner heliosphere in February 2020, making its first close pass at 0.5 AU while carrying instruments to measure the solar wind, magnetic fields, and high-energy particles.