1 day / second
0.5 AU
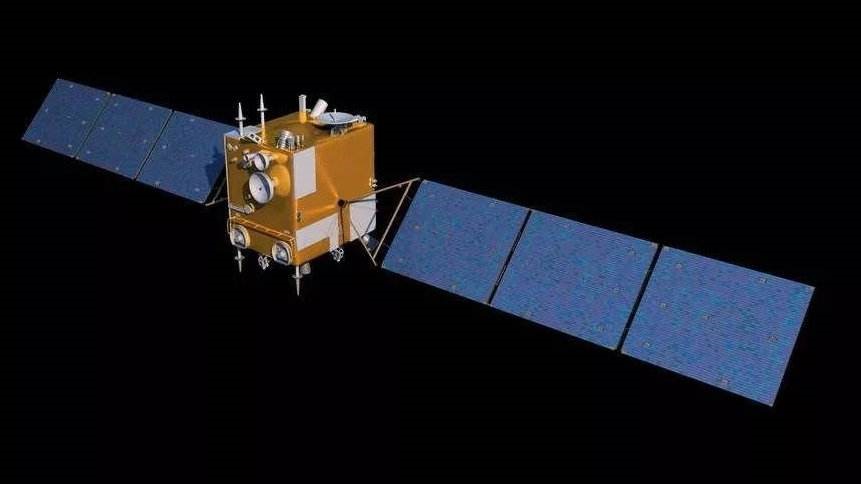
Chang'e 6
Spacecraft
A planned Chinese lunar mission scheduled for 2024 that aims to become the first spacecraft to return samples from the far side of the Moon.
Key Facts
organization | CNSA |
orbital regime | Inner System |
learn more | Wikipedia |
launched | 2024-05-03 |
returned | 2024-06-25 |
launch mass | 8,350 kg |
Mission Timeline
Launched
May 3, 2024 at 09:27 UTC
Luna (The Moon)
Lander
The robotic Chang'e 6 lander will attempt the first-ever landing on the Moon's far side in 2024, aiming to collect and return lunar samples from the South Pole-Aitken basin.
Returned
June 25, 2024 at 06:07 UTC
The lunar sample return mission successfully landed on the far side of the Moon, collected samples, and returned them safely to Earth on June 25, 2024, marking the first-ever recovery of material from the Moon's far side.
Related Spacecraft
Chang'e 1
Launched in 2007
Launched in 2007, Chang'e 1 became the first Chinese lunar orbiter, mapping the Moon's surface and chemical composition during its 16-month mission before being intentionally crashed into the lunar surface in March 2009.
Chang'e 2
Launched in 2010
Following its 2010 launch, Chang'e 2 mapped the Moon's surface in high resolution, flew by asteroid 4179 Toutatis, and became China's first spacecraft to reach the Sun-Earth Lagrange point L2.
Chang'e 4
Launched in 2018
A robotic spacecraft that achieved the first soft landing on the lunar far side in January 2019, deploying the Yutu-2 rover to explore the South Pole-Aitken basin and conduct pioneering radio astronomy observations from the Moon's surface.
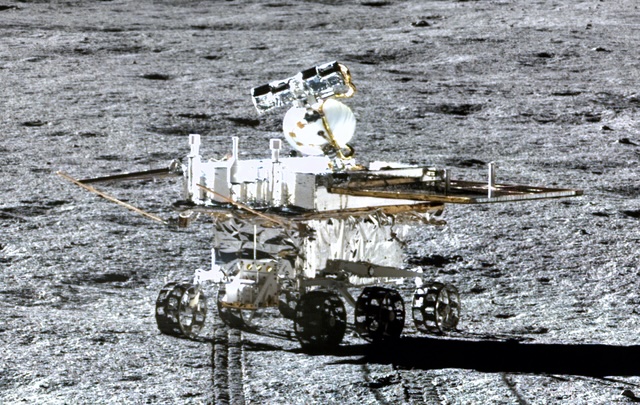
Yutu-2
Launched in 2018
A robotic lunar rover that landed on the far side of the Moon in January 2019 as part of the Chang'e 4 mission, becoming the first spacecraft to make a soft landing on the lunar far side and continuing to operate while exploring the South Pole-Aitken Basin.
Chang'e 5
Launched in 2020
A robotic lunar probe that successfully landed on the Moon in December 2020, collected about 1.7 kilograms of lunar samples from Oceanus Procellarum, and returned them to Earth, marking the first lunar sample return since 1976.