1 day / second
0.5 AU
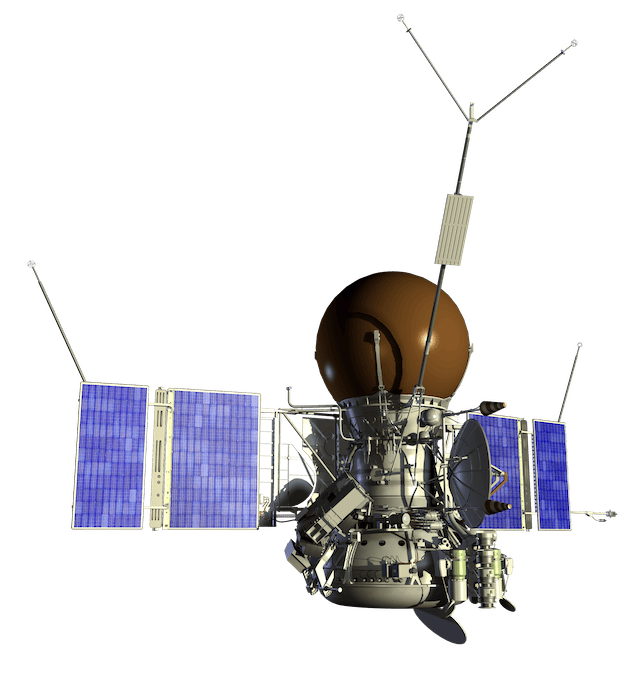
Magellan
Spacecraft
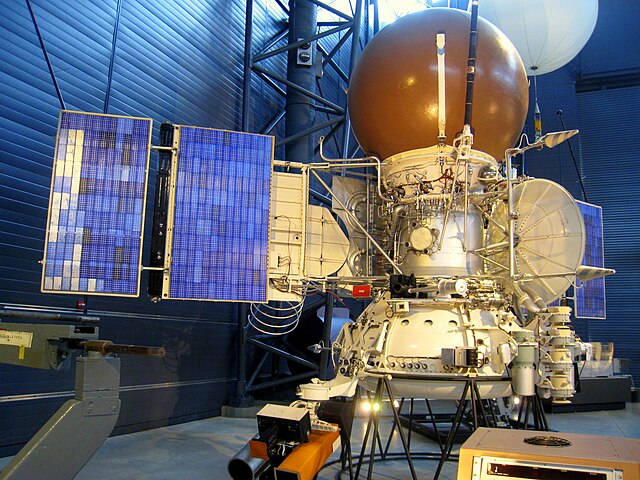
A pioneering Venus-mapping spacecraft launched in 1989 that used radar to peer through the planet's thick clouds, producing detailed maps of 98% of the surface before plunging into the atmosphere in 1994.
Key Facts
organization | NASA |
orbital regime | Inner System |
learn more | Wikipedia |
launched | 1989-05-04 |
decommissioned | 1994-10-13 |
launch mass | 3,445 kg |
power | 1,030 watts |
Mission Timeline
Launched
May 4, 1989 at 18:47 UTC
Venus
Orbiter
After entering orbit around Venus in August 1990, Magellan mapped 98% of the planet's surface using radar imaging over three mapping cycles, revealing a landscape dominated by volcanic features and impact craters before deliberately plunging into the atmosphere in 1994.
Decommissioned
October 13, 1994 at 10:05 UTC
After completing its mission to map 98% of Venus' surface using radar, Magellan was intentionally plunged into the planet's atmosphere where it vaporized after sending its final signal at 10:05 UTC on October 13, 1994.